sed (stream editor)是 Linux 上强大的流编辑器,用程序的方式来编辑文本,非常强大。
基础使用
常用参数
sed [OPTION]... {script-only-if-no-other-script} [input-file]...
A file name of - refers to the standard input stream.
-n, –quite, –slient to suppress output
-e script, –expression=script 指定脚本
-f script-file, –file=script-file 指定脚本文件
-i, edit file in-place. 默认sed 编辑器不会修改文件的数据,修改后的数据发送到 STDOUT。使用 -i 直接修改文件。
-E, -r, –regexp-extended, Use extended regular expressions rather than basic regular expressions.
-s, –separate
-u, —unbuffered Buffer both input and output as minimally as practical. (This is particularly useful if the input is coming from the likes of tail -f, and you wish to see the transformed output as soon as possible.)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 指定脚本文件
$ sed -f script1.sed data1.txt
$ sed ’s/hello/world/’ input.txt > output.txt
$ sed -e ’s/hello/world/’ input.txt > output.txt
$ sed --expression=’s/hello/world/’ input.txt > output.txt
$ echo ’s/hello/world/’ > myscript.sed
$ sed -f myscript.sed input.txt > output.txt
$ sed --file=myscript.sed input.txt > output.txt
# sed 默认输出到标准输出,使用 -i 直接编辑文件
$ sed -i ’s/hello/world/’ file.txt
替换 s
s/pattern/replacement/flags
默认只替换每行中出现的第一处。有4种可用的替换标记:
- 数字,表明新文本将替换第几处模式匹配的地方;
- g,全部替换;
- p,打印;
- w file,将替换结果写到文件中;
p 替换标记常和 -n 选项一起使用。-n 选项禁止 sed 编辑器输出,二者配合使用就是只输出被替换命令修改过的行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
$ echo "This is a test" | sed 's/test/big test/'
This is a big test
# 使用多个命令
$ sed 's/brown/green/; s/dog/cat/' data2.txt
# test.txt 中的 dog 替换为 cat
$ sed 's/dog/cat/' test.txt
# 替换每行的第二处
$ sed 's/dog/cat/2' test.txt
# 替换所有
$ sed 's/dog/cat/g' test.txt
# 替换第2个以后的dog
$ sed 's/dog/cat/2g' test.txt
# 打印替换的行
$ sed -n 's/dog/cat/p' test.txt
# 替换的行写到文件中
$ sed 's/dog/cat/w out.txt' test.txt
# 替换 /etc/passwd 中的 shell
$ sed 's/\/bin\/bash/\/bin\/csh/' /etc/passwd
# 上面不容易看懂,可以指定其它字符串分隔符
$ sed 's!/bin/bash!/bin/csh!' /etc/passwd
# 在开头插入
$ seq 5 | sed 's/^/# /g'
# 1
# 2
# 3
# 4
# 5
# 在尾部插入
$ seq 5 | sed 's/$/# /g'
1#
2#
3#
4#
5#
使用地址
以数字形式表示行区间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 替换第2行
$ sed '2s/dog/cat/' test.txt
# 替换第2-3行
$ sed '2,3s/dog/cat/' test.txt
# 替换从第2行开始的所有行,$ 表示最后一行
$ sed '2,$s/dog/cat/' test.txt
# 执行多条命令
$ sed '3,${
> s/fox/elephant/
> s/dog/cat/
> }' data1.txt
# +3 表示之后的三行
$ seq 5 | sed '/2/,+3s/^/# /g'
1
# 2
# 3
# 4
# 5
使用文本模式过滤器:/pattern/command
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 修改用户 xiaocan 的 shell
$ sed '/xiaocan/s/bash/zsh/' /etc/passwd
# 使用正则表达式
$ echo "This is a test" | sed -n "/test/p"
# 从行首匹配
$ echo "Books are great" | sed -n "/^Book/p"
# 从行尾匹配
$ echo "Books are great" | sed -n "/great$/p"
删除行 d
使用 d 删除行:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 删除第三行
$ seq 10 | sed '3d'
# 删除第1-3行
$ seq 10 | sed '1,3d'
# 删除包含 4 的行
$ seq 4 | sed '/4/d'
# 删除包含2 和 3 之间的所有行
$ seq 10 | sed '/2/,/3/d'
# 会删除包含 2 开始的所有行(找不到 11)
$ sed 10 | sed '/2/,/11/d'
# ^$ 匹配空白行,下面的例子会删除空白行
$ sed '/^$/d' data.txt
插入文本 a i
sed '[address]command\new line'
i 在指定行前增加一个新行;
a 在指定行后增加一个新行;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# insert
$ echo "Test line 2" | sed 'i\Test line 1'
Test line 1
Test line 2
# 可以不添加 \
$ echo "Test line 2" | sed 'i Test line 1'
Test line 1
Test line 2
# append
$ echo "Test line 2" | sed 'a\Test line 1'
Test line 2
Test line 1
# 指定行
$ seq 3 | sed '1i\0'
0
1
2
3
# 插入空白行
$ seq 3 | sed '2i\ \'
$ seq 3 | sed '2i\\'
# 在最后一行添加
$ seq 3 | sed '$a\4'
1
2
3
4
# 添加多行,使用 \ 分割
$ seq 3 | sed '$a\4\
> 5\
> 6'
1
2
3
4
5
6
修改行 c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ seq 5 | sed '3c\change this line'
1
2
change this line
4
5
# 用多行替换这一行
$ sed 5 | sed '2,3c/change this line'
1
change this line
4
5
转换命令 y
一对一字符替换:[address]y/inchars/outchars/,inchars 和 outchars 的长度要一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$ seq 3 | sed 'y/123/789/'
7
8
9
# 默认就是全局替换,
$ echo "This 1 is a test of 1 try." | sed 'y/123/456/'
This 4 is a test of 4 try.
打印 p
p 打印文本行;
= 打印行号;
l 列出行(list),可以打印数据流中的文本和不可打印的 ASCII 字符。
p 常和 -n 一起使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
$ seq 5 | sed -n '/5/p'
5
$ seq 5 | sed -n '2,3p'
2
3
$ seq 5 | sed -n '/2/{
# 打印原来行
> p
# 打印替换后的行
> s/2/222/p
> }'
2
222
# 打印行号
$ sed '=' data2.txt
1
One line of test text.
2
Two line of test text.
3
Three line of test text.
$ sed -n '/One/{
> =
> p
> }' data2.txt
1
One line of test text.
# 测试 l
$ cat data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
$ sed -n 'l' data2.txt
One line of test text.$
Two line of test text.$
Three line of test text.$
Four\tline\tof\ttest\ttext.$
写入文件 w
[address]w filename
1
2
3
$ seq 10 | sed '1,3w test.txt'
$ sed '/xiaocan/w xiaocan.txt' /etc/passwd
读取数据 r
[address]r filename
地址只能用单独一个行号或者文本模式地址。读取文件,插入到指定地址之后。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
$ cat data4.txt
This is a test of the test script;
This is the second test of the test script;
$ seq 3 | sed '2r data4.txt'
1
2
This is a test of the test script;
This is the second test of the test script;
3
# 在最后添加
$ seq 3 | sed '$r data4.txt'
$ sed '/LIST/{
# 替换占位符
> r data1.txt
# 删除原来的占位符
> d
> }' out.txt
排除命令 !
使用 ! 用排除命令:
1
2
3
4
# 不打印包含3 的行
$ seq 3 | sed -n '/3/!p'
1
2
退出码 q
0 Successful completion.
1 Invalid command, invalid syntax, invalid regular expression
2 输入的文件不能打开(文件找不到或者没有权限)
4 An I/O error, or a serious processing error during runtime, GNU sed aborted immediately.
使用 Q 或者 q 指定退出码:
1
2
3
4
5
$ echo | sed ’Q42’ ; echo $?
42
# 输出直到遇到 foo 开头的行
$ sed '/^foo/q42' input.txt > output.txt
模式替换 & \1
& 可以用来代表替换命令中匹配的模式。
1
2
3
$ echo "The cat sleeps in his hat." | sed 's/.at/"&"/g'
The "cat" sleeps in his "hat".
sed 用圆括号来定义替换模式中的子模式,然后可以用 \1 \2 等引用匹配的字模式。
1
2
3
4
5
6
# 圆括号需要转义
$ echo "The System Administrator manual" | sed 's/\(System\) Administrator/\1 User/'
The System User manual
$ echo "The furry hat is pretty" | sed 's/furry \(.at\)/\1/'
The hat is pretty
命令分组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 对3行到第6行,执行命令/This/d
$ sed '3,6 {/This/d}' pets.txt
# 对3行到第6行,匹配/This/成功后,再匹配/fish/,成功后执行d命令
$ sed '3,6 {/This/{/fish/d}}' pets.txt
# 从第一行到最后一行,如果匹配到This,则删除之;如果前面有空格,则去除空格
$ sed '1,${/This/d;s/^ *//g}' pets.txt
多行命令
N:将数据流中的下一行加进来创建一个多行组来处理。
D:删除多行组中的一行。
P:打印多行组中的一行。
next 命令 N
n 移动到下一行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
$ cat data1.txt
This is the header line.
This is a data line.
This is the last line.
# 删除第一行后的那行
$ sed '/header/{n ; d}' data1.txt
This is the header line.
This is a data line.
This is the last line.
N 将下一行与当前行合并处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
$ cat data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
# 合并两行
$ sed '/Two/{N ; s/\n/ /}' data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text. Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
# 如何将下面的 System Administraor 替换成 Desktop User 呢?
# 注意第一行和第二行跨行了
$ cat data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
# 为啥两处的替换都没有生效呢?
# 第一个是因为不匹配;第二个是因为读取第三行的时候,没有下一行了,所以sed命令就停止了
$ sed 'N ; s/System Administrator/Desktop User/' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
# 中间添加一个通配符,可以匹配换行,第一处成功替换了
$ sed 'N ; s/System.Administrator/Desktop User/' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux Desktop User's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
# 使用 $! 排除最后一行
$ sed '$!N ; s/System\nAdministrator/Desktop\nUser/; s/System Administrator/Desktop User/' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux Desktop
User's group meeting will be held.
All Desktop Users should attend.
# N 前面的替换匹配单行的,N 后面的替换匹配多行的,这样就可以了。
$ sed 's/System Administrator/Desktop User/ ; N ; s/System\nAdministrator/Desktop\nUser/' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux Desktop
User's group meeting will be held.
All Desktop Users should attend.
# 但是,如果文本是这样该任何替换呢?
$ sed 's/System Administrator/Desktop User/ ; N ; s/System\nAdministrator/Desktop\nUser/' data3.txt
All Desktop Users should attend.
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
多行删除 D
D 删除模式空间中的第一行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$ cat data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
# 删除了第一行
$ sed 'N; /System\nAdministrator/D' data3.txt
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
多行打印 P
p 打印模式空间中的第一行。
1
2
$ sed -n 'N; /System\nAdministrator/P' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Pattern space & hold space
pattern space 是 sed 用来处理文本的缓冲区。hold space 是另外一个区域,可以用来临时保存一些行。
h 将 pattern space 复制到 hold space
H 将 pattern space 附加到 hold space
g 将 hold space 复制到 pattrn space
G 将 hold space 附加到 pattern sapce
x 交换 pattern space 和 hold space 的内容
通常,在使用 h 和 H 命令之后,还要用 g 和 G 命令把内容拿回来。
反转文件中行的顺序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
$ cat data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
$ sed -n '{1!G ; h ; $p}' data2.txt
Four line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Two line of test text.
One line of test text.
# 或者
$ sed '{1!G ; h ; $!d}' data2.txt
Four line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Two line of test text.
One line of test text.
# tac 命令也可以反转行
$ tac data2.txt
Four line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Two line of test text.
One line of test text.
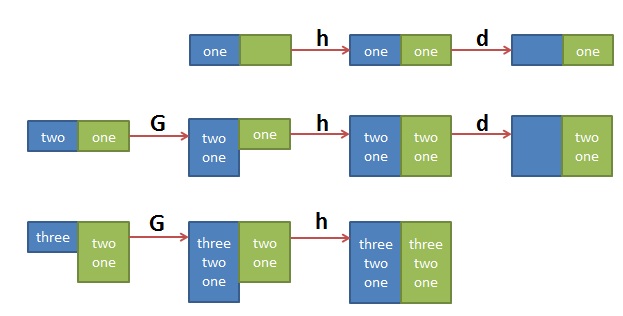
下图展示了 {1!G ; h ; $!d} 的执行流程:
改变流
分支 b
sed 编辑器提供了一种方法,可以基于地址、地址模式或地址区间排除一整块命令。
[address]b [label] address 参数指定哪些行会触发分支命令。label 指定了要跳转的位置,如果没有,会跳转到脚本的结尾。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
$ cat data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
# 第2行和第三行不执行替换命令
$ sed '{2,3b ; s/line/Line/ ; s/text/line/}' data2.txt
One Line of test line.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four Line of test line.
# 匹配行执行标签之后的命令,其它行执行所有的命令
$ sed '{/One/b jump1; s/test text/no jump/
> :jump1
> s/line/Line/}' data2.txt
One Line of test text.
Two Line of no jump.
Three Line of no jump.
Four Line of no jump.
测试 t
t 测试命令会根据替换命令的结果跳转到某个标签。相当于 if-then 语句。
[address]t [label]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
$ cat data2.txt
One line of test text.
Two line of test text.
Three line of test text.
Four line of test text.
# 不匹配的行执行 t 后面的替换命令
$ sed '{
> s/One/matched/
> t
> s/line/no match/
> }' data2.txt
matched line of test text.
Two no match of test text.
Three no match of test text.
Four no match of test text.
$ echo "This, is, a, test, to, remove, commas." | sed -n '{
> :start
> s/,//1p
> t start
> }'
This is, a, test, to, remove, commas.
This is a, test, to, remove, commas.
This is a test, to, remove, commas.
This is a test to, remove, commas.
This is a test to remove, commas.
This is a test to remove commas.
使用示例
加倍行间距
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
$ cat data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
# G 会将 hold space 内容附加到 pattern space 内容后面,默认是空行
$ sed 'G' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
$
# 最后一行不添加空白行
$ sed '$!G' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
$
# 如果文件中存在空白行,先删除空白行,再添加
$ sed '/^$/d ; $!G' data3.txt
On Tuesday, the Linux System
Administrator's group meeting will be held.
All System Administrators should attend.
打印行号
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 打印行号,但是不够美观
$ sed '=' data2.txt
1
One line of test text.
2
Two line of test text.
3
Three line of test text.
# 删除行号和内容之间的换行符
$ sed '=' data2.txt | sed 'N ; s/\n/ /'
1 One line of test text.
2 Two line of test text.
3 Three line of test text.
打印末尾行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
$ sed -n '$p' data2.txt
Three line of test text.
# 打印最后的5行,比较难理解,还是直接用 seq 10 | tail -5 吧
$ seq 10 | sed '{
> :start
> $q ; N ; 6,$D
> b start
> }'
6
7
8
9
10
删除行
删除连续的空白行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
$ cat data5.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
$
$ sed '/./,/^$/!d' data5.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
区间 /./ 到 /^$/ ,开始地址匹配任何含有至少一个字符的行,结束地址匹配一个空行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
# 打印非空行
$ sed -n '/./p' data5.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
删除开头的空白行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
$ cat data6.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
$
# 从有内容的行到结尾的行不删除,其它都删除
$ sed '/./,$!d' data6.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
删除结尾的空白行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
$ cat data6.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
$
$ sed '{
> :start
> /^\n*$/{$d ; N ; b start }
> }' data6.txt
This is line one.
This is line two.
This is line Three.
This is line four.
$
这个脚本里面还有花括号,这允许在整个脚本中将一些命令分组。该命令组会被应用在指定的地址模式上。
地址模式能够匹配含有0个或多个换行符的行。如果找到这样的行,而且还是最后一行,就删除它。如果不是最后一行,N 命令会将下一行附加到它后面,分支命令会跳到循环起始位置重新开始。
删除标签
1
2
3
4
5
6
$ cat HTML.txt
<b>This</b> is what <span style="text-decoration: underline;">I</span> meant. Understand?
# 其中的'[^>]' 指定了除了>的字符重复0次或多次。
$ sed 's/<[^>]*>//g' HTML.txt
This is what I meant. Understand?
参考
https://www.gnu.org/software/sed/manual/sed.pdf
http://sed.sourceforge.net/